Supercomputers
The COMPSs Framework can be installed in any Supercomputer by installing its packages as in a normal distribution. The packages are ready to be reallocated so the administrators can choose the right location for the COMPSs installation.
However, if the administrators are not willing to install COMPSs through the packaging system, we also provide a COMPSs zipped file containing a pre-build script to easily install COMPSs. Next subsections provide further information about this process.
Prerequisites
In order to successfully run the installation script some dependencies must be present on the target machine. Administrators must provide the correct installation and environment of the following software:
Autotools
BOOST
Java 8 JRE
The following environment variables must be defined:
JAVA_HOME
BOOST_CPPFLAGS
The tracing system can be enhanced with:
PAPI, which provides support for harware counters
MPI, which speeds up the tracing merge (and enables it for huge traces)
Installation
To perform the COMPSs Framework installation please execute the following commands:
$ # Check out the last COMPSs release
$ wget http://compss.bsc.es/repo/sc/stable/COMPSs_<version>.tar.gz
$ # Unpackage COMPSs
$ tar -xvzf COMPSs_<version>.tar.gz
$ # Install COMPSs at your preferred target location
$ cd COMPSs
$ ./install [options] <targetDir> [<supercomputer.cfg>]
$ # Clean downloaded files
$ rm -r COMPSs
$ rm COMPSs_<version>.tar.gz
The installation script will install COMPSs inside the given <targetDir>
folder and it will copy the <supercomputer.cfg> as default configuration.
It also provides some options to skip the installation of optional features or
bound the installation to an specific python version. You can see the available
options with the following command.
$ ./install --help
Attention
If the <targetDir> folder already exists it will be automatically erased.
After completing the previous steps, administrators must ensure that the nodes have passwordless ssh access. If it is not the case, please contact the COMPSs team at support-compss@bsc.es.
The COMPSs package also provides a compssenv file that loads the
required environment to allow users work more easily with COMPSs. Thus,
after the installation process we recommend to source the
<targetDir>/compssenv into the users .bashrc.
Once done, remember to log out and back in again to end the installation process.
Configuration
To maintain the portability between different environments, COMPSs has a
pre-built structure of scripts to execute applications in Supercomputers.
For this purpose, users must use the enqueue_compss script provided in the
COMPSs installation and specify the supercomputer configuration with
--sc_cfg flag.
When installing COMPSs for a supercomputer, system administrators must define
a configuration file for the specific Supercomputer parameters.
This document gives and overview about how to modify the configuration files
in order to customize the enqueue_compss for a specific queue system and
supercomputer.
As overview, the easier way to proceed when creating a new configuration is to
modify one of the configurations provided by COMPSs. System sdministrators can
find configurations for LSF, SLURM, PBS and SGE as well as
several examples for Supercomputer configurations in
<installation_dir>/Runtime/scripts/queues.
For instance, the configuration for the MareNostrum IV Supercomputer and the
Slurm queue system, can be used as base file for new supercomputer and queue
system cfgs. Sysadmins can modify these files by changing the flags,
parameters, paths and default values that corresponds to your supercomputer.
Once, the files have been modified, they must be copied to the queues folder
to make them available to the users. The following paragraph describe more
in detail the scripts and configuration files
If you need help, contact support-compss@bsc.es.
COMPSs Queue structure overview
All the scripts and cfg files shown in Figure 4 are located
in the <installation_dir>/Runtime/scripts/ folder.
enqueue_compss and launch_compss (launch.sh in the figure) are in
the user subfolder and submit.sh and the cfgs are located in queues.
There are two types of cfg files: the queue system cfg files, which are
located in queues/queue_systems; and the supercomputers.cfg files, which
are located in queues/supercomputers.
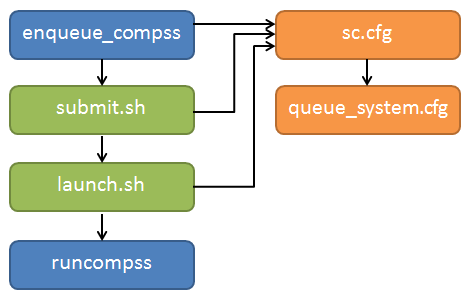
Figure 4 Structure of COMPSs queue scripts. In Blue user scripts, in Green queue scripts and in Orange system dependant scripts
Configuration Files
The cfg files contain a set of bash variables which are used by the other scripts. On the one hand, the queue system cfgs contain the variables to indicate the commands used by the system to submit and spawn processes, the commands or variables to get the allocated nodes and the directives to indicate the number of nodes, processes, etc. Below you can see an example of the most important variable definition for Slurm
# File: Runtime/scripts/queues/queue_systems/slurm.cfg
################################
## SUBMISSION VARIABLES
################################
# Variables to define the queue system directives.
# The are built as #${QUEUE_CMD} ${QARG_*}${QUEUE_SEPARATOR}value (submit.sh)
QUEUE_CMD="SBATCH"
SUBMISSION_CMD="sbatch"
SUBMISSION_PIPE="< "
SUBMISSION_HET_SEPARATOR=' : '
SUBMISSION_HET_PIPE=" "
# Variables to customize the commands know job id and allocated nodes (submit.sh)
ENV_VAR_JOB_ID="SLURM_JOB_ID"
ENV_VAR_NODE_LIST="SLURM_JOB_NODELIST"
QUEUE_SEPARATOR=""
EMPTY_WC_LIMIT=":00"
QARG_JOB_NAME="--job-name="
QARG_JOB_DEP_INLINE="false"
QARG_JOB_DEPENDENCY_OPEN="--dependency=afterany:"
QARG_JOB_DEPENDENCY_CLOSE=""
QARG_JOB_OUT="-o "
QARG_JOB_ERROR="-e "
QARG_WD="--workdir="
QARG_WALLCLOCK="-t"
QARG_NUM_NODES="-N"
QARG_NUM_PROCESSES="-n"
QNUM_PROCESSES_VALUE="\$(expr \${num_nodes} \* \${req_cpus_per_node})"
QARG_EXCLUSIVE_NODES="--exclusive"
QARG_SPAN=""
QARG_MEMORY="--mem="
QARG_QUEUE_SELECTION="-p "
QARG_NUM_SWITCHES="--gres="
QARG_GPUS_PER_NODE="--gres gpu:"
QARG_RESERVATION="--reservation="
QARG_CONSTRAINTS="--constraint="
QARG_QOS="--qos="
QARG_OVERCOMMIT="--overcommit"
QARG_CPUS_PER_TASK="-c"
QJOB_ID="%J"
QARG_PACKJOB="packjob"
################################
## LAUNCH VARIABLES
################################
# Variables to customize worker process spawn inside the job (launch_compss)
LAUNCH_CMD="srun"
LAUNCH_PARAMS="-n1 -N1 --nodelist="
LAUNCH_SEPARATOR=""
CMD_SEPARATOR=""
HOSTLIST_CMD="scontrol show hostname"
HOSTLIST_TREATMENT="| awk {' print \$1 '} | sed -e 's/\.[^\ ]*//g'"
################################
## QUEUE VARIABLES
## - Used in interactive
## - Substitute the %JOBID% keyword with the real job identifier dinamically
################################
QUEUE_JOB_STATUS_CMD="squeue -h -o %T --job %JOBID%"
QUEUE_JOB_RUNNING_TAG="RUNNING"
QUEUE_JOB_NODES_CMD="squeue -h -o %N --job %JOBID%"
QUEUE_JOB_CANCEL_CMD="scancel %JOBID%"
QUEUE_JOB_LIST_CMD="squeue -h -o %i"
QUEUE_JOB_NAME_CMD="squeue -h -o %j --job %JOBID%"
################################
## CONTACT VARIABLES
################################
CONTACT_CMD="ssh"
To adapt this script to your queue system, you just need to change the variable value to the command, argument or value required in your system. If you find that some of this variables are not available in your system, leave it empty.
On the other hand, the supercomputers cfg files contains a set of variables to indicate the queue system used by a supercomputer, paths where the shared disk is mounted, the default values that COMPSs will set in the project and resources files when they are not set by the user and flags to indicate if a functionality is available or not in a supercomputer. The following lines show examples of this variables for the MareNostrum IV supercomputer.
# File: Runtime/scripts/queues/supercomputers/mn.cfg
################################
## STRUCTURE VARIABLES
################################
QUEUE_SYSTEM="slurm"
################################
## ENQUEUE_COMPSS VARIABLES
################################
DEFAULT_EXEC_TIME=10
DEFAULT_NUM_NODES=2
DEFAULT_NUM_SWITCHES=0
MAX_NODES_SWITCH=18
MIN_NODES_REQ_SWITCH=4
DEFAULT_QUEUE=default
DEFAULT_MAX_TASKS_PER_NODE=-1
DEFAULT_CPUS_PER_NODE=48
DEFAULT_IO_EXECUTORS=0
DEFAULT_GPUS_PER_NODE=0
DEFAULT_FPGAS_PER_NODE=0
DEFAULT_WORKER_IN_MASTER_CPUS=24
DEFAULT_WORKER_IN_MASTER_MEMORY=50000
DEFAULT_MASTER_WORKING_DIR=.
DEFAULT_WORKER_WORKING_DIR=local_disk
DEFAULT_NETWORK=infiniband
DEFAULT_DEPENDENCY_JOB=None
DEFAULT_RESERVATION=disabled
DEFAULT_NODE_MEMORY=disabled
DEFAULT_JVM_MASTER=""
DEFAULT_JVM_WORKERS="-Xms16000m,-Xmx92000m,-Xmn1600m"
DEFAULT_JVM_WORKER_IN_MASTER=""
DEFAULT_QOS=default
DEFAULT_CONSTRAINTS=disabled
################################
## Enabling/disabling passing
## requirements to queue system
################################
DISABLE_QARG_MEMORY=true
DISABLE_QARG_CONSTRAINTS=false
DISABLE_QARG_QOS=false
DISABLE_QARG_OVERCOMMIT=true
DISABLE_QARG_CPUS_PER_TASK=false
DISABLE_QARG_NVRAM=true
HETEROGENEOUS_MULTIJOB=false
################################
## SUBMISSION VARIABLES
################################
MINIMUM_NUM_NODES=1
MINIMUM_CPUS_PER_NODE=1
DEFAULT_STORAGE_HOME="null"
DISABLED_STORAGE_HOME="null"
################################
## LAUNCH VARIABLES
################################
LOCAL_DISK_PREFIX="/scratch/tmp"
REMOTE_EXECUTOR="none" # Disable the ssh spawn at runtime
NETWORK_INFINIBAND_SUFFIX="-ib0" # Hostname suffix to add in order to use infiniband network
NETWORK_DATA_SUFFIX="-data" # Hostname suffix to add in order to use data network
SHARED_DISK_PREFIX="/gpfs/"
SHARED_DISK_2_PREFIX="/.statelite/tmpfs/gpfs/"
DEFAULT_NODE_MEMORY_SIZE=92
DEFAULT_NODE_STORAGE_BANDWIDTH=450
MASTER_NAME_CMD=hostname # Command to know the mastername
ELASTICITY_BATCH=true
To adapt this script to your supercomputer, you just need to change the variables to commands paths or values which are set in your system. If you find that some of this values are not available in your system, leave them empty or as they are in the MareNostrum IV.
How are cfg files used in scripts?
The submit.sh is in charge of getting some of the arguments from
enqueue_compss, generating the a temporal job submission script for the
queue_system (function create_normal_tmp_submit) and performing the
submission in the scheduler (function submit).
The functions used in submit.sh are implemented in common.sh.
If you look at the code of this script, you will see that most of the code is
customized by a set of bash vars which are mainly defined in the cfg files.
For instance the submit command is customized in the following way:
eval ${SUBMISSION_CMD} ${SUBMISSION_PIPE}${TMP_SUBMIT_SCRIPT}
Where ${SUBMISSION_CMD} and ${SUBMISSION_PIPE} are defined in the
queue_system.cfg. So, for the case of Slurm, at execution time it is
translated to something like sbatch < /tmp/tmp_submit_script
The same approach is used for the queue system directives defined in the submission script or in the command to get the assigned host list.
The following lines show the examples in these cases.
#${QUEUE_CMD} ${QARG_JOB_NAME}${QUEUE_SEPARATOR}${job_name}
In the case of Slurm in MN, it generates something like #SBATCH --job-name=COMPSs
host_list=\$(${HOSTLIST_CMD} \$${ENV_VAR_NODE_LIST}${env_var_suffix} ${HOSTLIST_TREATMENT})
The same approach is used in the launch_compss script where it is using
the defined vars to customize the project.xml and resources.xml file
generation and spawning the master and worker processes in the assigned resources.
At first, you should not need to modify any script. The goal of the cfg files is that sysadmins just require to modify the supercomputers cfg, and in the case that the used queue system is not in the queue_systems, folder it should create a new one for the new one.
If you think that some of the features of your system are not supported in the current implementation, please contact us at support-compss@bsc.es. We will discuss how it should be incorporated in the scripts.
Post installation
To check that COMPSs Framework has been successfully installed you may run:
$ # Check the COMPSs version
$ runcompss -v
COMPSs version <version>
For queue system executions, COMPSs provides several prebuild queue scripts than can be accessible throgh the enqueue_compss command. Users can check the available options by running:
$ enqueue_compss -h
Usage: /apps/COMPSs/2.9/Runtime/scripts/user/enqueue_compss [queue_system_options] [COMPSs_options] application_name application_arguments
* Options:
General:
--help, -h Print this help message
--heterogeneous Indicates submission is going to be heterogeneous
Default: Disabled
Queue system configuration:
--sc_cfg=<name> SuperComputer configuration file to use. Must exist inside queues/cfgs/
Default: default
Submission configuration:
General submision arguments:
--exec_time=<minutes> Expected execution time of the application (in minutes)
Default: 10
--job_name=<name> Job name
Default: COMPSs
--queue=<name> Queue name to submit the job. Depends on the queue system.
For example (MN3): bsc_cs | bsc_debug | debug | interactive
Default: default
--reservation=<name> Reservation to use when submitting the job.
Default: disabled
--constraints=<constraints> Constraints to pass to queue system.
Default: disabled
--qos=<qos> Quality of Service to pass to the queue system.
Default: default
--cpus_per_task Number of cpus per task the queue system must allocate per task.
Note that this will be equal to the cpus_per_node in a worker node and
equal to the worker_in_master_cpus in a master node respectively.
Default: false
--job_dependency=<jobID> Postpone job execution until the job dependency has ended.
Default: None
--storage_home=<string> Root installation dir of the storage implementation
Default: null
--storage_props=<string> Absolute path of the storage properties file
Mandatory if storage_home is defined
Normal submission arguments:
--num_nodes=<int> Number of nodes to use
Default: 2
--num_switches=<int> Maximum number of different switches. Select 0 for no restrictions.
Maximum nodes per switch: 18
Only available for at least 4 nodes.
Default: 0
--agents=<string> Hierarchy of agents for the deployment. Accepted values: plain|tree
Default: tree
--agents Deploys the runtime as agents instead of the classic Master-Worker deployment.
Default: disabled
Heterogeneous submission arguments:
--type_cfg=<file_location> Location of the file with the descriptions of node type requests
File should follow the following format:
type_X(){
cpus_per_node=24
node_memory=96
...
}
type_Y(){
...
}
--master=<master_node_type> Node type for the master
(Node type descriptions are provided in the --type_cfg flag)
--workers=type_X:nodes,type_Y:nodes Node type and number of nodes per type for the workers
(Node type descriptions are provided in the --type_cfg flag)
Launch configuration:
--cpus_per_node=<int> Available CPU computing units on each node
Default: 48
--gpus_per_node=<int> Available GPU computing units on each node
Default: 0
--fpgas_per_node=<int> Available FPGA computing units on each node
Default: 0
--io_executors=<int> Number of IO executors on each node
Default: 0
--fpga_reprogram="<string> Specify the full command that needs to be executed to reprogram the FPGA with
the desired bitstream. The location must be an absolute path.
Default:
--max_tasks_per_node=<int> Maximum number of simultaneous tasks running on a node
Default: -1
--node_memory=<MB> Maximum node memory: disabled | <int> (MB)
Default: disabled
--node_storage_bandwidth=<MB> Maximum node storage bandwidth: <int> (MB)
Default: 450
--network=<name> Communication network for transfers: default | ethernet | infiniband | data.
Default: infiniband
--prolog="<string>" Task to execute before launching COMPSs (Notice the quotes)
If the task has arguments split them by "," rather than spaces.
This argument can appear multiple times for more than one prolog action
Default: Empty
--epilog="<string>" Task to execute after executing the COMPSs application (Notice the quotes)
If the task has arguments split them by "," rather than spaces.
This argument can appear multiple times for more than one epilog action
Default: Empty
--master_working_dir=<path> Working directory of the application
Default: .
--worker_working_dir=<name | path> Worker directory. Use: local_disk | shared_disk | <path>
Default: local_disk
--worker_in_master_cpus=<int> Maximum number of CPU computing units that the master node can run as worker. Cannot exceed cpus_per_node.
Default: 24
--worker_in_master_memory=<int> MB Maximum memory in master node assigned to the worker. Cannot exceed the node_memory.
Mandatory if worker_in_master_cpus is specified.
Default: 50000
--worker_port_range=<min>,<max> Port range used by the NIO adaptor at the worker side
Default: 43001,43005
--jvm_worker_in_master_opts="<string>" Extra options for the JVM of the COMPSs Worker in the Master Node.
Each option separed by "," and without blank spaces (Notice the quotes)
Default:
--container_image=<path> Runs the application by means of a container engine image
Default: Empty
--container_compss_path=<path> Path where compss is installed in the container image
Default: /opt/COMPSs
--container_opts="<string>" Options to pass to the container engine
Default: empty
--elasticity=<max_extra_nodes> Activate elasticity specifiying the maximum extra nodes (ONLY AVAILABLE FORM SLURM CLUSTERS WITH NIO ADAPTOR)
Default: 0
--automatic_scaling=<bool> Enable or disable the runtime automatic scaling (for elasticity)
Default: true
--jupyter_notebook=<path>, Swap the COMPSs master initialization with jupyter notebook from the specified path.
--jupyter_notebook Default: false
--ipython Swap the COMPSs master initialization with ipython.
Default: empty
Runcompss configuration:
Tools enablers:
--graph=<bool>, --graph, -g Generation of the complete graph (true/false)
When no value is provided it is set to true
Default: false
--tracing=<level>, --tracing, -t Set generation of traces and/or tracing level ( [ true | basic ] | advanced | scorep | arm-map | arm-ddt | false)
True and basic levels will produce the same traces.
When no value is provided it is set to 1
Default: 0
--monitoring=<int>, --monitoring, -m Period between monitoring samples (milliseconds)
When no value is provided it is set to 2000
Default: 0
--external_debugger=<int>,
--external_debugger Enables external debugger connection on the specified port (or 9999 if empty)
Default: false
--jmx_port=<int> Enable JVM profiling on specified port
Runtime configuration options:
--task_execution=<compss|storage> Task execution under COMPSs or Storage.
Default: compss
--storage_impl=<string> Path to an storage implementation. Shortcut to setting pypath and classpath. See Runtime/storage in your installation folder.
--storage_conf=<path> Path to the storage configuration file
Default: null
--project=<path> Path to the project XML file
Default: /apps/COMPSs/2.9//Runtime/configuration/xml/projects/default_project.xml
--resources=<path> Path to the resources XML file
Default: /apps/COMPSs/2.9//Runtime/configuration/xml/resources/default_resources.xml
--lang=<name> Language of the application (java/c/python)
Default: Inferred is possible. Otherwise: java
--summary Displays a task execution summary at the end of the application execution
Default: false
--log_level=<level>, --debug, -d Set the debug level: off | info | api | debug | trace
Warning: Off level compiles with -O2 option disabling asserts and __debug__
Default: off
Advanced options:
--extrae_config_file=<path> Sets a custom extrae config file. Must be in a shared disk between all COMPSs workers.
Default: null
--trace_label=<string> Add a label in the generated trace file. Only used in the case of tracing is activated.
Default: None
--comm=<ClassName> Class that implements the adaptor for communications
Supported adaptors:
├── es.bsc.compss.nio.master.NIOAdaptor
└── es.bsc.compss.gat.master.GATAdaptor
Default: es.bsc.compss.nio.master.NIOAdaptor
--conn=<className> Class that implements the runtime connector for the cloud
Supported connectors:
├── es.bsc.compss.connectors.DefaultSSHConnector
└── es.bsc.compss.connectors.DefaultNoSSHConnector
Default: es.bsc.compss.connectors.DefaultSSHConnector
--streaming=<type> Enable the streaming mode for the given type.
Supported types: FILES, OBJECTS, PSCOS, ALL, NONE
Default: NONE
--streaming_master_name=<str> Use an specific streaming master node name.
Default: null
--streaming_master_port=<int> Use an specific port for the streaming master.
Default: null
--scheduler=<className> Class that implements the Scheduler for COMPSs
Supported schedulers:
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.fifodatalocation.FIFODataLoctionScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.fifonew.FIFOScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.fifodatanew.FIFODataScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.lifonew.LIFOScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.components.impl.TaskScheduler
└── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.loadbalancing.LoadBalancingScheduler
Default: es.bsc.compss.scheduler.loadbalancing.LoadBalancingScheduler
--scheduler_config_file=<path> Path to the file which contains the scheduler configuration.
Default: Empty
--library_path=<path> Non-standard directories to search for libraries (e.g. Java JVM library, Python library, C binding library)
Default: Working Directory
--classpath=<path> Path for the application classes / modules
Default: Working Directory
--appdir=<path> Path for the application class folder.
Default: /home/group/user
--pythonpath=<path> Additional folders or paths to add to the PYTHONPATH
Default: /home/group/user
--base_log_dir=<path> Base directory to store COMPSs log files (a .COMPSs/ folder will be created inside this location)
Default: User home
--specific_log_dir=<path> Use a specific directory to store COMPSs log files (no sandbox is created)
Warning: Overwrites --base_log_dir option
Default: Disabled
--uuid=<int> Preset an application UUID
Default: Automatic random generation
--master_name=<string> Hostname of the node to run the COMPSs master
Default:
--master_port=<int> Port to run the COMPSs master communications.
Only for NIO adaptor
Default: [43000,44000]
--jvm_master_opts="<string>" Extra options for the COMPSs Master JVM. Each option separed by "," and without blank spaces (Notice the quotes)
Default:
--jvm_workers_opts="<string>" Extra options for the COMPSs Workers JVMs. Each option separed by "," and without blank spaces (Notice the quotes)
Default: -Xms1024m,-Xmx1024m,-Xmn400m
--cpu_affinity="<string>" Sets the CPU affinity for the workers
Supported options: disabled, automatic, user defined map of the form "0-8/9,10,11/12-14,15,16"
Default: automatic
--gpu_affinity="<string>" Sets the GPU affinity for the workers
Supported options: disabled, automatic, user defined map of the form "0-8/9,10,11/12-14,15,16"
Default: automatic
--fpga_affinity="<string>" Sets the FPGA affinity for the workers
Supported options: disabled, automatic, user defined map of the form "0-8/9,10,11/12-14,15,16"
Default: automatic
--fpga_reprogram="<string>" Specify the full command that needs to be executed to reprogram the FPGA with the desired bitstream. The location must be an absolute path.
Default:
--io_executors=<int> IO Executors per worker
Default: 0
--task_count=<int> Only for C/Python Bindings. Maximum number of different functions/methods, invoked from the application, that have been selected as tasks
Default: 50
--input_profile=<path> Path to the file which stores the input application profile
Default: Empty
--output_profile=<path> Path to the file to store the application profile at the end of the execution
Default: Empty
--PyObject_serialize=<bool> Only for Python Binding. Enable the object serialization to string when possible (true/false).
Default: false
--persistent_worker_c=<bool> Only for C Binding. Enable the persistent worker in c (true/false).
Default: false
--enable_external_adaptation=<bool> Enable external adaptation. This option will disable the Resource Optimizer.
Default: false
--gen_coredump Enable master coredump generation
Default: false
--python_interpreter=<string> Python interpreter to use (python/python2/python3).
Default: python Version: 2
--python_propagate_virtual_environment=<true> Propagate the master virtual environment to the workers (true/false).
Default: true
--python_mpi_worker=<false> Use MPI to run the python worker instead of multiprocessing. (true/false).
Default: false
--python_memory_profile Generate a memory profile of the master.
Default: false
* Application name:
For Java applications: Fully qualified name of the application
For C applications: Path to the master binary
For Python applications: Path to the .py file containing the main program
* Application arguments:
Command line arguments to pass to the application. Can be empty.
If none of the pre-build queue configurations adapts to your infrastructure (lsf, pbs, slurm, etc.) please contact the COMPSs team at support-compss@bsc.es to find out a solution.
If you are willing to test the COMPSs Framework installation you can run any of the applications available at our application repository https://github.com/bsc-wdc/apps. We suggest to run the java simple application following the steps listed inside its README file.
For further information about either the installation or the usage please check the README file inside the COMPSs package.